|
|
SynchroSym |
|
|
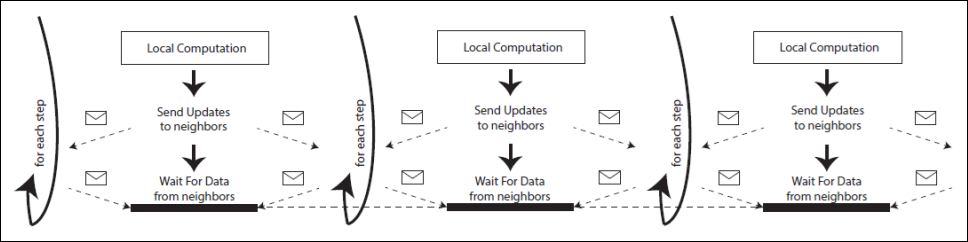
In a parallel computing scenario, the
synchronization overhead, needed to coordinate the execution on the parallel
computing nodes, can significantly impair the overall execution performance.
Typically, synchronization is achieved by adopting a global synchronization
involving all the nodes. In many application domains, though, a looser
synchronization schema, namely, local synchronization, can be exploited, in which each
node needs to synchronize only with a subset of the other nodes. SynchroSym is a
simulator written in MatlabŪ purposely developed to assess the execution
performance of parallel computing nodes that require to synchronize with each
other by adopting either local or global synchronization. The parallel computation
is considered to be step-based,
and synchronization is required at the end of each step. In SynchroSym, the computing nodes can be organized
along a mono-dimensional
structure having N nodes, in which each node needs to synchronize with a
number of left and right neighbours, and along a two-dimensional lattice with Nr rows and
Nc columns in which each node needs to synchronize with its Von Neumann
neighborhood (i.e., its north, south, east and west neighbors) or with its
Moore neighborhood (which includes also the four diagonal neighbors). A simulation run is configured by specifying the
number of involved computational nodes, the organization of the nodes, the
number of computing steps composing the whole computation, and the
probability distribution function used to assess the computation time for
each node at each computational step. |
|
|
Download
files · Mono-dimensional simulator · Two-dimensional simulator |
|
Authors: Franco Cicirelli (cicirelli@icar.cnr.it) - Andrea Giordano (giordano@icar.cnr.it) - Carlo Mastroianni (mastroianni@icar.cnr.it) |